OGG Vorbis
Main Source:
Media Container
Section titled “Media Container”A media container is a file that encapsulates multiple types of media data, such as audio, video, text, and metadata together. This is achieved through multiplexing, which in this context means combining (interleaving) multiple types of data into a single continuous data stream. This approach simplifies the handling of multiple data types (e.g., synchronizing video and audio). In contrast, separating them into multiple files or parts within the same file requires additional headers and synchronization information.
A media container format supports multiple codecs for encoding or decoding the corresponding format.
OGG is multimedia container format. It uses Vorbis audio codec and Theora video codec, in which both are lossy compression format.
OGG Structure
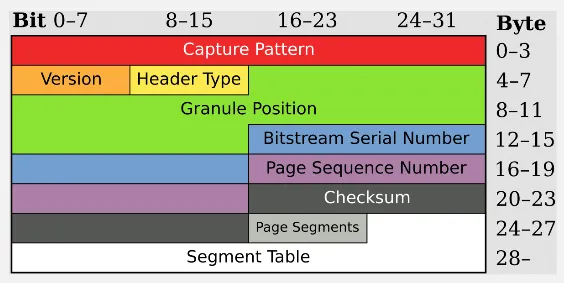
Section titled “OGG Structure”OGG file consists of a sequence of pages. Each page begins with a 27-byte header, followed by a variable-length payload. Each page size is generally between 4 and 64 kilobytes.
- OGG Header: The OGG file begins with an OGG header, which provides essential information about the file and its streams. The header includes details, such as the OGG format version, the number of streams within the file, and the serial numbers assigned to each stream.
- Page Header: Each page starts with a page header that contains metadata about the page itself. The header includes information such as the granule position, which represents the position of the data within the stream, and the page sequence number.
- Packet Data: Following the page header, the page contains one or more packets of data. Each packet represents a chunk of encoded audio, video, text, or other multimedia data. The packets may belong to different streams within the file.
- Page Segments: The page segments section follows the packet data and specifies the sizes of the individual packets within the page. It allows for variable-sized packets within a fixed-sized page.
- Page CRC Checksum: Each page concludes with a checksum value, which is used to verify the integrity of individual page.
- Metadata: Metadata can include details such as track titles, artist/author information, album/movie information, genres, and more. The metadata is typically stored in dedicated packets within the stream.
OGG page header
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ogg
OGG Vorbis
Section titled “OGG Vorbis”Vorbis is the specific codecs for audio data in OGG file. Vorbis codec divide audio data into small sections called “blocks” or “windows.” Each block typically contains a few milliseconds of audio.
Encoding Process
Section titled “Encoding Process”- Psychoacoustic Modeling: The Vorbis codec applies a psychoacoustic model to analyze the audio within each block. This model takes into account the characteristics of human hearing and discard the less important audio.
- Transform: The audio data within each block is transformed from the time domain into the frequency domain using the modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT). The modified DCT is used to process overlapping blocks of audio or video data. This transformation will map the audio to frequency domain.
- Quantization: The transformed audio data is quantized, meaning the amplitudes of the frequency components are approximated and represented with fewer bits.
- Encoding: The quantized audio data is further processed and encoded using variable bit rate encoding. The codec allocates more bits to preserve important audio details and fewer bits for less important parts, based on the psychoacoustic analysis.
- Bit stream Generation: The encoded audio data, along with metadata such as track information and tags, is packaged into a bit stream or sequence of bit to the OGG container format.