MP3
Main Source:
MP3 (MPEG Audio Layer-3) is a digital audio format that uses lossy compression, resulting in much smaller file than the uncompressed WAV.
MP3 Compression
Section titled “MP3 Compression”MP3 is known for its compression to achieve a 75 to 95% reduction in size.
- Transform Coding: MP3 uses the modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT), which can handle overlapping signals.
- Psychoacoustics Modeling: Psychoacoustic modeling removes less relevant data by analyzing human hearing. This may include removing frequencies and components that are masked by louder or more important sounds.
- Quantization: Quantization is the process of assigning a limited number of bits to represent the amplitude of the audio samples. In MP3, quantization process also takes account the psychoacoustic modeling.
- Huffman Encoding: Huffman encoding replace frequently occurring audio values with short code identifier and longer codes to less frequent values, to reduce the overall number of bits required to represent the data.
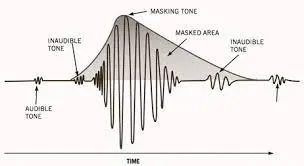
Source: https://ledgernote.com/blog/q-and-a/how-does-mp3-compression-work/
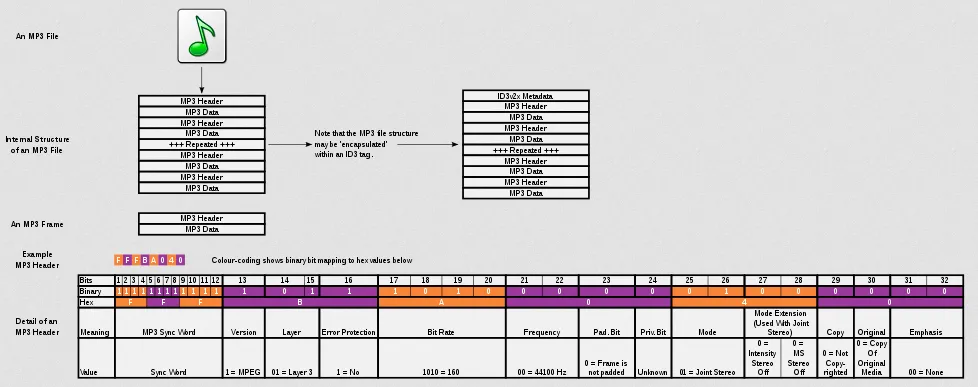
MP3 Structure
Section titled “MP3 Structure”MP3 file is made up of a sequence of frames, each of which consists of a header and a data block.
- Header: The file begins with an MP3 header that contains important information about the file, such as the audio format, bit rate, sampling rate, stereo/mono mode, and more. The header provides essential details for decoding and playing the file correctly.
- Audio Frames: Each frame represents a small segment of audio and contains compressed audio data. The size of each frame can vary depending on the bit rate and other settings used during encoding. The frames are usually consistent in size throughout the file.
- Side Information: For each audio frame, there is corresponding side information that provides details about the frame’s structure and compression parameters. This information includes data such as the scale factors, Huffman coding tables, and stereo/mono mode information.
- Main Data: The main data section contains the compressed audio data. It includes the actual audio samples that have been encoded and compressed using various techniques.
- Ancillary Data: MP3 files can also include ancillary data, such as ID3 tags, which store additional metadata about the audio file, such as the song title, artist, album, and other details. These tags provide information that can be displayed by media players.