BMP
Main Source:
Bitmap (BMP) is a raster image format that stores pixel data for an image. BMP stores pixel data in binary format. BMP are generally uncompressed, meaning the original data doesn’t undergo compression process.
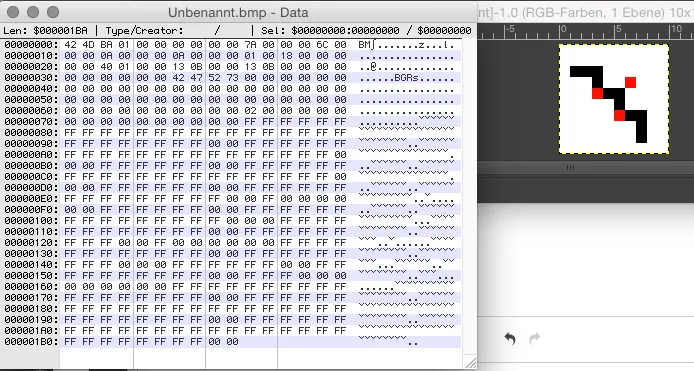
raw data inside a BMP file
Source: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/33483708/understanding-bmp-file
BMP Structure
Section titled “BMP Structure”BMP file contains several components:
- File Header: File begins with a fixed-size header that provides general information about the file, such as the file type, size, and offset to the pixel data.
- DIB Header: The DIB (Device Independent Bitmap) contains specific information about the image, such as its width and height in pixels, color depth, compression method (if any), and color palette.
- Color Palette (optional): For images with indexed color (color depths of 8 bits or fewer), an optional color palette may be present. The color palette is an array of color entries that maps pixel values to specific colors.
- Pixel Data: After the headers, the file contains the actual pixel data. The pixel data represents the image itself, with each pixel’s color or intensity information stored in a specific format based on the color depth. For example, in a 24-bit color depth BMP file, each pixel is represented by three bytes, typically in the order of blue, green, and red (BGR).
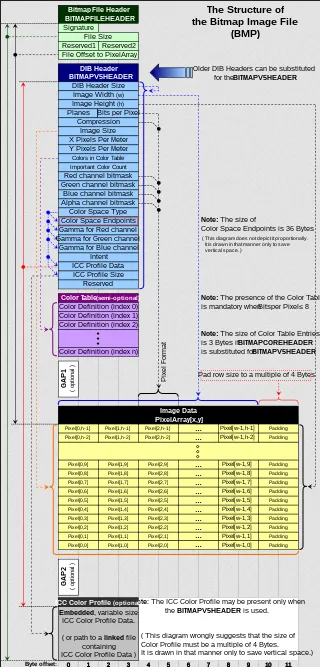
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BMP_file_format
Indexed Color
Section titled “Indexed Color”Indexed color is a technique to store and represent color using a predefined color palette (usually limited). Instead of directly specifying the color of each individual pixel, indexed color images represent each pixel with an index value that corresponds to a specific color in the palette.
For example, in RGB, we may represent the color red in a pixel with (255, 0, 0). This results in each pixel to occupy 24-bit. With indexed color, we can represent the same color with fewer bits. However, indexed color usually restrict the amount of color in the palette.
We may define a color palette with 256 possible color. Therefore, we will need a minimum 8 bits to be able to access every color by its index in the palette. This is the reason indexed color favor image with less distinct color.
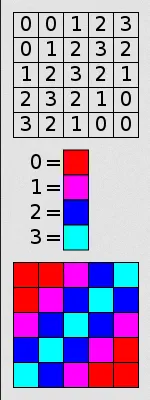
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indexed_color
This image above represent the 5×5 grid using 2-bit color palette. This means it needs 2-bit to index a color, and can represent up to color.