MD
Main Source:
.md file format or Markdown is a markup language used to style plain text with format elements, such as heading, list, images, bold, italic, underlined text, hyperlinks, etc. Markdown can be easily converted into HTML. In fact, it supports HTML and CSS styling within it.
Markdown uses a set of symbol to indicate which part of the plain text to be formatted. For example, surrounding a text around double * like **Hello** will make the text bold. Using # will create a heading based on the amount of #.
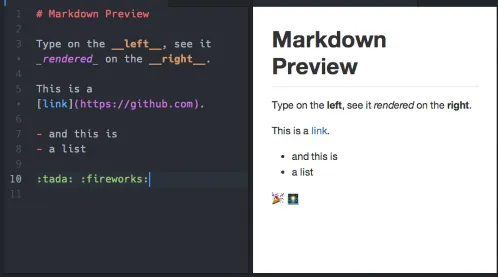
Source: https://dev.to/developer_anand/learn-basic-markdown-33nl
Markdown Parsing
Section titled “Markdown Parsing”Markdown files with its format element is parsed and converted into the corresponding styled HTML elements.
- Tokenization: Markdown text is broke down into tokens. Tokens are the elements of the Markdown syntax, such as headers, lists, paragraphs.
- Parsing: Tokens are identified and analyzed to build a hierarchical representation of the document. It identifies the nesting of elements, such as nested lists, and creates a data structure (usually tree) to represent the document’s structure.
- Conversion: The Markdown processor applies transformation rules to convert the Markdown tokens and structure into the desired output format. For example, when it sees
#behind a text, it may generate HTML heading tags (<h1>), and fill the corresponding text inside it. - Rendering: The converted HTML is rendered and displayed by web browser.
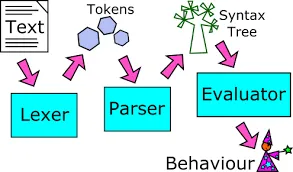
Source: https://accu.org/journals/overload/26/146/balaam_2532/