TXT
Main Source:
A .txt file format, or simply a text file, is a very simple format used to store plain text data. It contains human-readable text without any specific formatting or metadata. The characters can be encoded in various scheme, such as ASCII or UTF-8.
The structure of a .txt file is very simple; it consists of a sequence of lines that vary in length, with each line terminated by a newline character (typically created by pressing the Enter key on a keyboard).
Different operating systems have different way to handle line endings. In Windows OS, a new line is represented as CRLF \r\n, while Linux uses just LF \n for new lines.
txt File Representation
Section titled “txt File Representation”.txt file are stored in binary data encoded with specific character encoding scheme. Typically, .txt file does not store metadata on the file itself. Any information about the file, is usually managed by the file system rather than being embedded in the file.
For example, consider a text file that uses ASCII encoding.
Hello, World!In ASCII, the letter “H” is represented by the decimal value 72, “e” by 101, “l” by 108, “o” by 111, comma (”,”) by 44, space by 32, and so on. Each decimal value is then mapped into its ASCII code. Typically, we don’t represent the ASCII code in raw binary, but rather in hexadecimal format.
hex: 48 65 6C 6C 6F 2C 20 57 6F 72 6C 64 21binary: 01001000 01100101 01101100 01101100 01101111 00101100 00100000 01010111 01101111 01110010 01101100 01100100 00100001The file system that handles it will reverse the process, turning the hexadecimal code into its corresponding ASCII symbols. However, discrepancy could occur when the text file is made and displayed in different operating systems. The OS may expect different encoding than ASCII, or it could use different conventions for line endings.
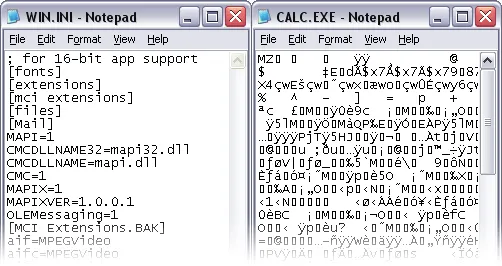
Source: https://www.thecrazyprogrammer.com/2018/05/difference-between-text-file-and-binary-file.html