Fast Fourier Transform
Main Source:
- Various source from Google and YouTube
Fast Fourier transform (FFT) algorithm is a fast and efficient algorithm for computing the Discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence of complex numbers. FFT improves a quadratic complexity algorithm to a linearithmic speed.
How does it work
Section titled “How does it work”There are few versions of FFT developed over time, the most common version is the radix-2 version which was originally described by Cooley-Tukey in 1965.
DFT Properties
Section titled “DFT Properties”DFT has some properties due to the nature of wave.
- Symmetry: When the input signal is real and even (symmetric), then the output will also be real and even (symmetric). Similarly, if the input signal is real and odd (antisymmetric), then the output will be imaginary and odd (antisymmetric).
- Periodicity: Periodicity property states that the output of DFT will repeat after a certain number of samples.
Using these properties, we can use it to perform a more efficient computation.
The Idea
Section titled “The Idea”The periodicity property can help reduce computation. Knowing that the output repeats at certain points allows us to avoid calculating samples outside that period. This makes us able to decompose the whole calculation into smaller calculation.
With the symmetry properties, we know that the second half of the signal is related to the first half, this allows us to derive the FFT result of the second half from the result of the first half.
For example, if a signal has period of 8 (meaning it repeat every 8 samples), we can divide it to 8 calculation. Then, for each period, only the first half of the DFT need to be computed, because the second half of the coefficients can be obtained by symmetrical property.
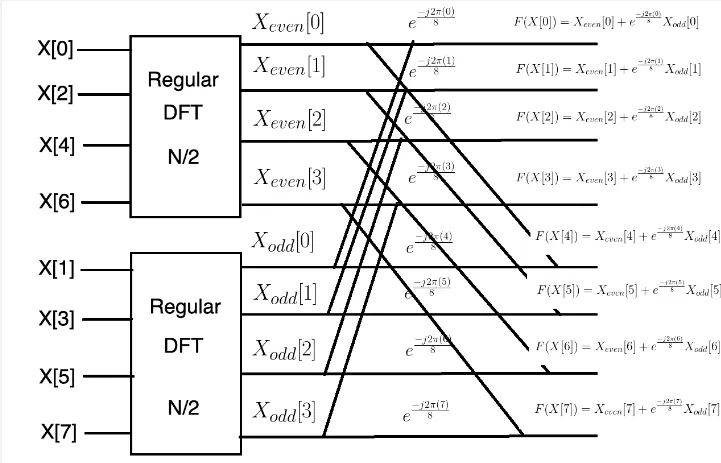
Source: https://towardsdatascience.com/fast-fourier-transform-937926e591cb
FFT algorithm use the divide-and-conquer algorithm strategy. FFT divides problem into smaller subproblems and solve it recursively, which makes computation more efficient.