Filtering
Main Source:
- Various source from Google and YouTube
In digital signal processing, filtering refers to the process of modifying or manipulating a digital signal to remove unwanted components or extract specific information. For example, unwanted components can be removed by applying techniques like the Fourier Transform, which separates signals based on their frequency components, allowing the removal of a particular frequency.
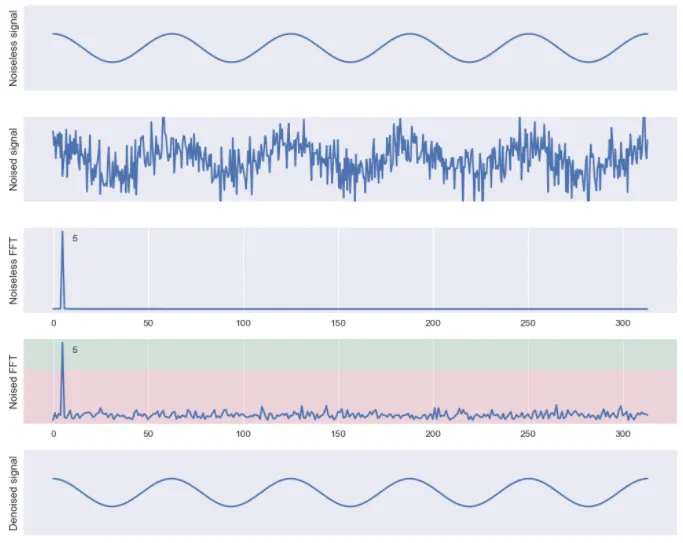
Source: https://towardsdatascience.com/the-fourier-transform-4-putting-the-fft-to-work-38dd84dc814
Applying filter works by selectively reducing or amplifying certain frequency components based on the desired filtering characteristics.
Some common filtering includes:
- Low-pass filter: Allows low-frequency components of a signal to pass through while reducing higher-frequency components.
- High-pass filter: Allows high-frequency components of a signal to pass through while or reducing lower-frequency components.
- Band-pass filter: Filters out both low and high-frequency content, allowing only the frequencies within the desired range to be present in the output signal.
- Band-stop filter: Reduces a specific range or band of frequencies while allowing frequencies outside that range to pass through.
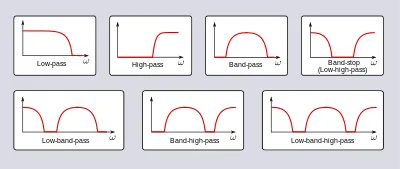
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Filter_(signal_processing)