GRU
- Illustrated Guide to LSTM’s and GRU’s: A step by step explanation — The AI Hacker
- Mengenal si GRU — Anak AI
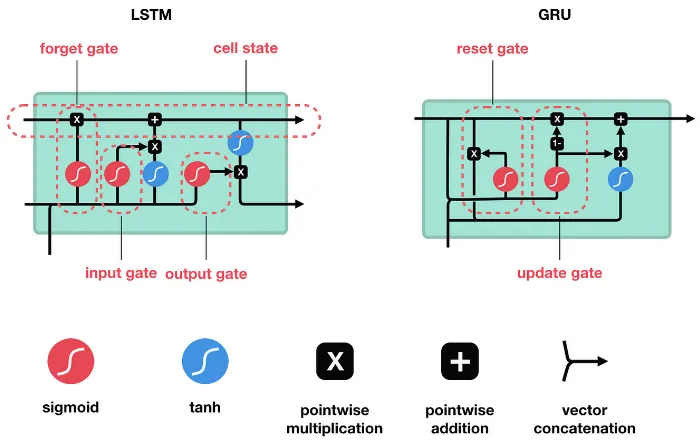
Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) is a type of recurrent neural network (RNN) and also the alternative of long short-term memory. GRU was developed to address LSTM limitation. LSTM has a complex architecture with different cell state and hidden state, making it computationally expensive.
LSTM vs GRU
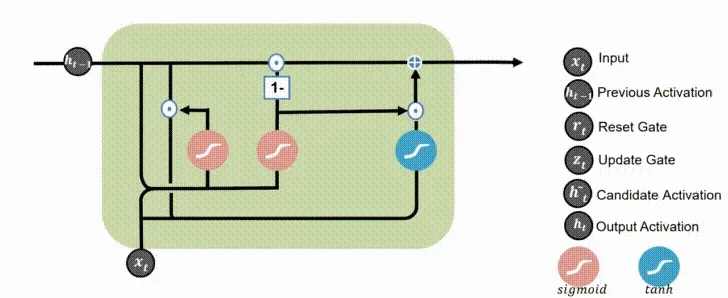
Section titled “LSTM vs GRU”GRU was designed to simplify LSTM architecture to reduce the number of parameters and computations involved. GRU doesn’t have cell state, instead the information from previous time step is passed in the hidden state. It also use 2 gate instead of 3:
- Reset Gate: The reset gate is like the forget gate in LSTM, it determines how much information from previous time step, passed from the hidden state is forgotten.
- Update Gate: Update gate can be thought as the forget gate and input gate combined. It determine how much information from previous time step is passed to next time step which is in the form of hidden state.
GRU Process
Section titled “GRU Process”-
Reset Gate: The current time step input () with the previous hidden state () are concatenated, it will be multipled by the reset gate weight (), added with reset gate bias term (), and transformed into the sigmoid activation function.
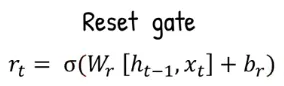
Source: https://youtu.be/mQ5CbaCK_Tg?si=wl4wDGuYneso475E&t=61 -
Candidate Activation: The result of reset gate will be multiplied with the previous hidden state (), the output will be concatenated with the current time step input (). Similarly, it will be multiplied by the candidate activation weight (), added with candidate activation bias term (), but transformed into the tanh activation function.
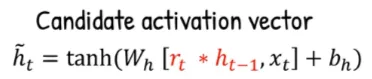
Source: https://youtu.be/mQ5CbaCK_Tg?si=Lt5xHS8Y8w6Tjt1H&t=70 -
Update Gate: Again, the previous hidden state () and the current input time step (), it will be multiplied with the update gate weight (), added with update gate bias term (), transformed into the sigmoid activation function.
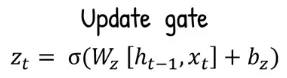
Source: https://youtu.be/mQ5CbaCK_Tg?si=eNrIPhBA171dZl1k&t=85 -
Hidden State Output: The current time step hidden state is calculated by the following formula.
- : This term uses the complement of update gate to calculate how much information from the previous hidden state should be forgotten.
- : This term represent how much information should be used for the next time step. The candidate activation is similar to input candidate in LSTM.
Both of them will be added and the result is the current time step hidden state.
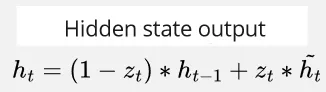
Source: https://youtu.be/mQ5CbaCK_Tg?si=3e1OgCWKpCDeyVgW&t=125 (with modification)
Below are the gif animation of GRU process
Source: Stacked_HG_CoordConvGRU - ayushgaud