Sorting
Main Source:
Sorting algorithms are algorithm that arranges a collection of elements based on specific order, such as ascending (increasing order) or descending (decreasing order). Sorting algorithms time and space complexity can vary from , , , or higher.
Bubble Sort
Section titled “Bubble Sort”Bubble sort is a very simple and intuitive sorting algorithm, it sorts elements by comparing each of them and swap them if they are in the wrong order.
Here is the pseudocode for bubble sort:
procedure BubbleSort(A: list) n:= length(A)
for i from 0 to n-2 do for j from 0 to n-i-2 do if A[j] > A[j+1] then swap A[j] and A[j+1] end if end for end forend procedureWe will have outer and inner loop, inside the inner loop, we will compare each adjacent element. Bubble sort results in best of time, average in , and worst in , with the space complexity being . The worst-case scenario occurs when we compare and swaps for every pair of elements in the input list.
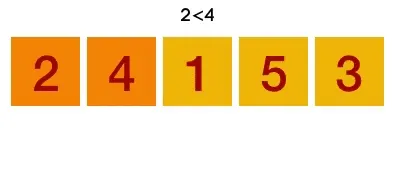
Source: https://www.doabledanny.com/bubble-sort-in-javascript
Selection Sort
Section titled “Selection Sort”Selection sort divides the input list into two parts: the sorted portion at the beginning and the unsorted portion at the end. The algorithm repeatedly find and select the smallest (or largest) element from the unsorted portion and swaps it with the element at the beginning of the unsorted portion. This process continues until the entire list is sorted.
procedure SelectionSort(A: list) n:= length(A)
for i from 0 to n-2 do minIndex:= i
for j from i+1 to n-1 do if A[j] < A[minIndex] then minIndex:= j end if end for
swap A[i] and A[minIndex] end forend procedureIn the pseudocode, we will find the index of the minimum (or maximum) element. After going to the entire list, we will swap the element at index i (outer loop) with the minimum element. This will be repeated for each element in the list. The algorithm always performs in time complexity for the best, average, and worst-case scenario, and uses constant memory, this is because, we will always need to swap each element in the list. While it isn’t the fastest, it has the advantage of doing fewer swaps compared to bubble sort.
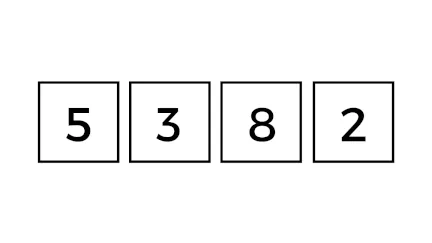
Source: https://matcha.fyi/selection-sort-javascript/
Insertion Sort
Section titled “Insertion Sort”Insertion sort builds the sorted portion of the list incrementally. It iterates through the input list, considering one element at a time and inserting it into its correct position within the already sorted portion of the list. The algorithm repeats this process until the entire list is sorted.
procedure InsertionSort(A: list) n:= length(A)
for i from 1 to n-1 do key:= A[i] j:= i - 1
while j >= 0 and A[j] > key do A[j + 1]:= A[j] j:= j - 1 end while
A[j + 1]:= key end forend procedureIt will iterate starting from index 1 to the last index of the list. We will also have extra index j, which is set as an index before i. If we encounter an element at index j which is greater than element at current index i (called the key), we will swap them, and then swap it again continuously backward until we achieved the correct order. After that, we will continue iterating the outer for loop.
Insertion sort results in best of time, average and worst in time, with the space complexity being . The worst-case scenario occurs when the input list is in reverse order. In this case, the algorithm has to perform the maximum number of comparisons and shifts for each element in order to insert it into its correct position within the sorted portion of the list.
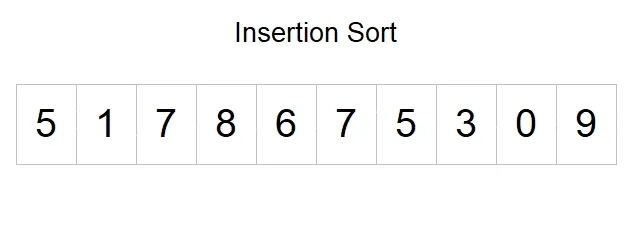
Source: Mark Bowman Chapter_15.01