Other Processing Units
Main Source:
- Graphics processing unit — Wikipedia
- Graphics Processor Unit (GPU) — Teach Computer Science
- Why an “if-else” statement (in GPUs code) will cut the performance in half — stackoverflow
- Vector processor — Wikipedia
- Single instruction, multiple data — Wikipedia
- Tensor Processing Unit — Wikipedia
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is a specialized processor designed to handle and accelerate the rendering, creation, and manipulation of images, videos, and graphics data.
Some aspects of GPU that makes it specialized:
- Parallel Processing: GPU are designed with many cores that can execute multiple tasks simultaneously. In contrast, CPU has less core, but each is more powerful. The parallel architecture enables GPUs to process data in parallel, making them highly efficient for tasks that can be broken down into smaller computational units.
- Dedicated Memory: Some GPU have their own dedicated memory called VRAM (Video RAM) or GDDR (Graphics Double Data Rate) memory. This memory is optimized for high-speed data access and is used to store textures, frame buffers, and other graphics-related data.
- Graphics Rendering Optimization: GPUs are specifically optimized for graphics rendering tasks. They have dedicated hardware components, such as texture mapping units, rasterizers, and shader cores, that accelerate the rendering pipeline.
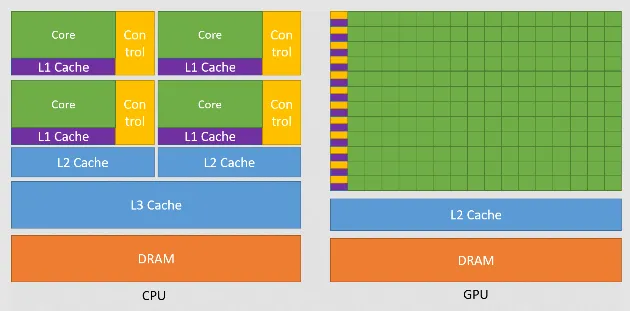
Source: https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-c-programming-guide/index.html
Other than graphics processing, GPU is also used for other tasks that involves a lot of computation that can be done on parallel such as neural networks.
GPU Components
Section titled “GPU Components”GPU consists of several components:
- Graphics and Compute Array (GCA): GCA contains the core processing unit of a GPU. It consists of multiple streaming multiprocessors (SM) or compute units that perform parallel computations.
- Compression Unit: Some GPUs incorporate compression units that can compress and decompress data to reduce memory bandwidth requirements. This can help improve performance by reducing memory bottlenecks and improving memory access efficiency.
- Graphics Memory Controller (GMC): GMC manages the interaction between the GPU and its dedicated graphics memory. It handles tasks such as memory allocation, data transfer, and memory bandwidth management.
- VGA BIOS: VGA BIOS is a firmware component stored on the GPU. It provides low-level initialization and configuration routines for the GPU during system boot-up. It is responsible for setting up the GPU’s initial state and ensuring compatibility with the system’s display capabilities.
- Bus Interface: Bus Interface is the component that connects the GPU to the computer’s system bus. It enables data transfer between the GPU and other system components, such as the CPU and system memory.
- Power Management Unit (PMU): The Power Management Unit is responsible for managing and regulating the power consumption of the GPU. It monitors power usage, adjusts clock frequencies, controls voltage levels, and implements power-saving features to optimize performance while minimizing power consumption.
- Video Processing Unit (VPU): VPU is a specialized component within some GPUs that handles video-related tasks. It includes functions such as video decoding, encoding, and post-processing.
- Display Interface: GPUs include display interfaces, such as HDMI, DisplayPort, or DVI. These interfaces provide the necessary signals and protocols for connecting monitors or other display devices to the GPU. They transmit video and audio data from the GPU to the display.
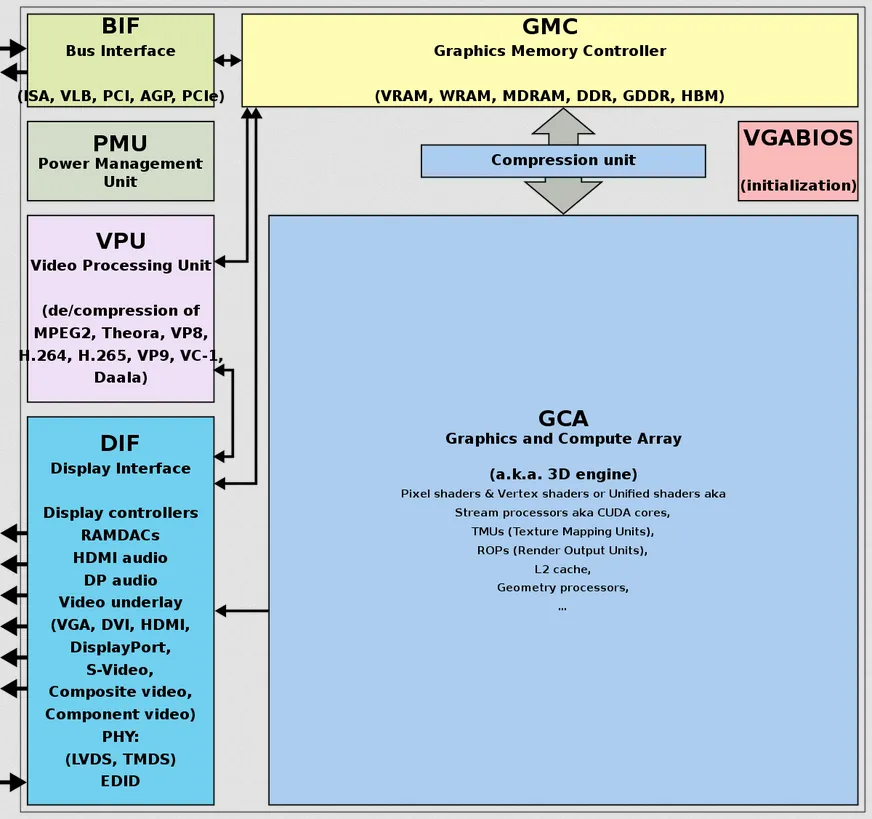
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graphics_processing_unit
-
Memory Hierarchy: GPUs have multiple levels of memory hierarchy:
- Global Memory: Global memory is the largest memory space in a GPU and is accessible by all threads. It is used to store data that needs to be shared across different threads.
- Shared Memory: Shared memory is a fast, low-latency memory space, but smaller than global memory, that is shared among threads within a thread block. It enables efficient data sharing and inter-thread communication.
- Texture Memory: Texture memory is a specialized read-only memory used for efficient texture mapping operations in graphics applications. It provides fast access to texture data for texture sampling.
- Constant Memory: Constant memory is a read-only memory space used for storing data that remains constant during kernel execution. It provides fast access to frequently used constants or configuration data.
-
Rasterizer: The rasterizer is a component responsible for converting geometric primitives (such as triangles) into pixels for display. It performs operations like clipping, culling, and interpolation of vertex attributes.
-
Texture Units: Texture units handle texture-related operations such as filtering, sampling, and interpolation. They are specialized hardware components designed for efficient texture mapping in graphics applications.
-
Frame & Pixel Buffer: These are temporary memory to store graphical data. The frame buffer represent the complete image on the screen, which is displayed currently, while the pixel buffer store pixel data temporarily during graphics processing tasks. The GPU continuously updates the buffer with new pixel data as it performs calculations and renders the scene.
GPU Programming
Section titled “GPU Programming”Traditional programming often rely on sequential processing, which utilizes a single processor core or a few cores. It focuses on optimizing the execution of instructions on a single thread or a limited number of threads.
The nature of parallelism in GPU architecture opens up a new field, GPU programming. Programmers can take advantage of the parallel architecture of GPU by breaking down tasks into smaller, independent units that can be executed in parallel, instead of sequential processing.
Compute Unified Device Architecture (CUDA), which is provided by NVIDIA, is an API that allow programmers to write code specifically for GPUs, these frameworks provide additional functionality and optimization techniques tailored for GPU architectures.
GPU programming typically uses less control flow construct like “if-else” statement. If-else statement is used to make a conditional branch based on some condition. GPU executes threads parallelly in a group called warps. When the processing encounter a branch, the threads may take different paths based on the condition. This leads to divergent execution, where threads within the same warp follow different code paths. Divergence can impact performance because threads that are not executing the same path are effectively serialized, leading to decreased parallelism.
Some branch may also take longer than the other branch, this will lead some thread idling to wait the other thread to finish, due to the parallelism of GPU.
Vector processing unit (VPU) is a type of CPU or processing unit that specializes in executing operations on vectors or arrays of data. There is also processor called scalar processors, which operate on single data element instead, like an integer or floating point number, while vector processors are designed to process multiple data elements simultaneously using vector instructions.
Vector processors excel at performing repetitive, data-parallel computations that can be efficiently executed in parallel. They are particularly well-suited for tasks that involve large-scale mathematical calculations, such as scientific simulations, computational physics, and data analytics.
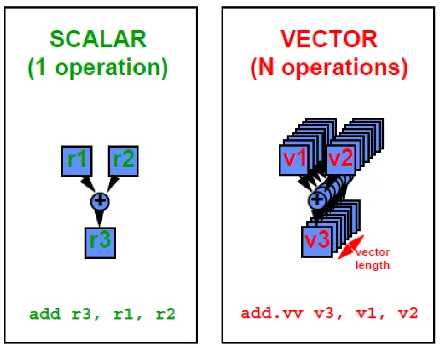
Source: https://www.cs.uic.edu/~ajayk/c566/VectorProcessors.pdf
Single Instruction, Multiple Data (SIMD) is parallel computing technique that allows a single instruction to be applied to multiple data elements simultaneously.
In SIMD processing, a single instruction is broadcasted to multiple processing units or execution lanes, each capable of processing a different data element from a vector or array.
Similar to GPU, SIMD is typically used for heavy computation tasks, but not for flow-control-heavy task that involves many conditional branches.
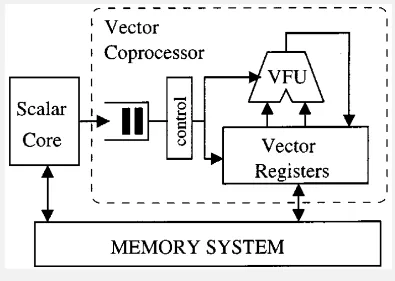
Vector Processor Architecture
Section titled “Vector Processor Architecture”Vector processors implement an instruction set for handling large one-dimensional data. Some features of vector processor:
- Vector Registers: Vector processors have dedicated vector registers that can hold multiple data elements in a single register. These registers are wider than traditional scalar registers to accommodate vector data. The number of elements that can be stored in a vector register is referred to as the vector length or vector width.
- Vector Instructions: Vector processors have specialized instructions, that can operate on the entire vector of data elements in a single instruction. These instructions define the operations to be performed on the vector data, such as arithmetic operations, logical operations, and data movement operations.
- Vector Functional Unit (VFU): VPU is the component in a vector processor that is responsible for executing specific arithmetic or logical operations on vector data. The VFU is a specialized hardware components optimized for vector operations.
- Vector Pipelines: Vector processors often include vector pipelines, which are composed of multiple stages that can process vector instructions in parallel. The pipeline stages are designed to carry out different phases of instruction execution, such as fetching instructions, decoding them, executing the operations, and writing back the results.
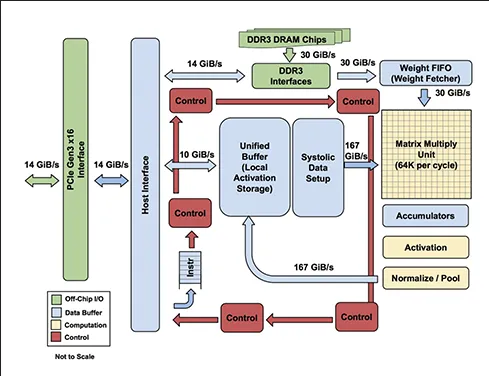
Tensor processing unit (TPU) is a specialized hardware accelerator developed by Google for accelerating machine learning workloads, particularly those involving neural networks.
Data used in machine learning based task often represented in matrix, or higher-dimensional array, in conclusion:
- Scalar processors: zero-dimensional data, such as “5”
- Vector processors: one-dimensional data, such as “[5, 3, 2]”
- TPU: n-dimensional data, such as “[[1, 2], [3, 5], [7, 8]]”, for two-dimensional data.
Some specialization TPU has:
- Reduced Precision: TPU are designed to perform computation that doesn’t require high precision, such as 8-bit or 16-bit floating-point formats, which is suitable for ML-based tasks. Using lower precision, we can reduce the memory bandwidth and storage requirements, which results in faster data transfer and processing times.
- Specialized Hardware & Architecture: TPU has hardware specific for doing machine learning tasks, it supports operations like normalization and pooling, which are commonly used in neural networks. TPU has special memory for storing learned weights that may be accessed frequently. Another key component of the hardware is the Matrix Multiply Unit (MMU), it is highly optimized processing unit for matrix computations, including convolution operations.