Lambda
Main Source:
Lambda is a data processing architecture designed to handle massive amounts of data in a fault-tolerant and scalable manner, combining another two techniques, namely batch processing and stream processing.
Batch Processing
Section titled “Batch Processing”Batch processing is a method to run software program, capable of running tasks that we call jobs in batches automatically by scheduling them at certain times. The method is typically used to process large amounts of data in a single operation. By processing, this may involve backup, filtering, sorting, or aggregating.
For example, a retail company wants to analyze its sales data to gain insights and make data-driven business decisions. The company can schedule batch processing which may involve collecting sales data, calculating total sales, identifying popular products, and generating sales reports. This process can be scheduled on daily basis, specifically at night, when the system experiences lower usage or during off-peak hours, to minimize user impact.
A batch processing job is defined by specific language, framework, or tools. The details to be specified:
- Data sources, location of data, operations to be performed, and other transformations.
- Dependencies or the order in which these steps need to be executed.
- Size of batch, how many data or work units that needs to be processed or done in one batch.
- Time and schedule of which the job executes.
- We can monitor the progress and performance of job, and set error or retry mechanism in case the execution fails.
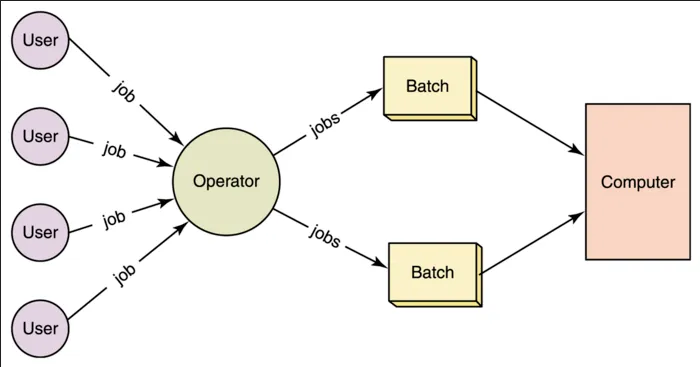
Source: https://estuary.dev/batch-data-processing/
Stream Processing
Section titled “Stream Processing”Stream processing (or real-time processing) is a method of data processing that involves continuously processing and analyzing streams, which is data or events produced or generated in real-time.
A typical process of stream processing:
-
Data Ingestion: Data is produced from various data sources, such as sensors, log files, message queues, or external systems. Data is imagined as water that flows through a system continuous and potentially infinite. They are treated as a continuous stream of events or records.
-
Windowing: Data can be processed in window, a way to group similar or related data within specific time intervals or fixed-size data subsets.
In time-based windowing, data may be divided into fixed-duration windows, such as 5-minute, 1-hour, or daily windows. On the other hand, fixed-size window may contain fixed number of events or data points, such as every 100 records or every 1,000 records.
-
Data Processing: The data is applied to series of operations or functions. Operations are typically pipelined or broke down into smaller, interconnected stages or steps.
-
Stateful Processing: Some stream processing may be stateful, meaning the data are related to each other, therefore we require a component that keeps track state or context of the processing. This can involve maintaining counters, aggregating statistics, or correlating events based on common attributes (e.g., detecting if specific sensor events is a valid gesture).
-
Output: After processing, stream processing systems generate outputs based on the defined operations and computations. This can include generating alerts, triggering actions, storing results in databases, sending data to external systems, or visualizing real-time analytics.
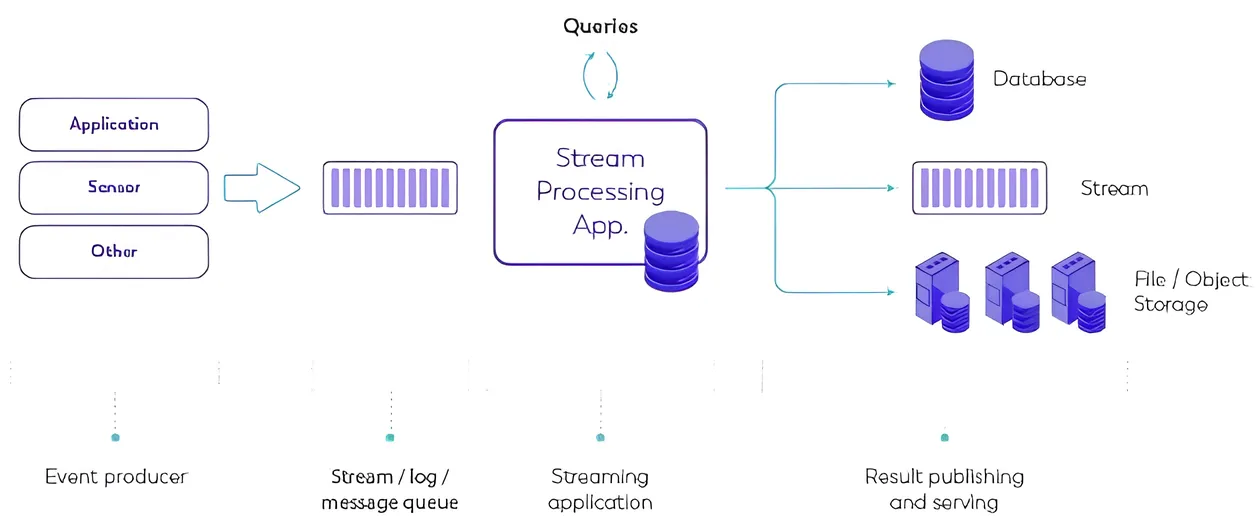
Source: https://www.ververica.com/what-is-stream-processing (cropped and upscaled)
Lambda Architecture
Section titled “Lambda Architecture”By combining batch and stream processing, lambda architecture enables the processing of all the available data within specific period, as well as the real-time produced data in one go.
Lambda works by dividing the batch and stream processing stage into three layers:
- Batch Layer: Handles the batch data that contains large volumes of historical data. Batch layer involve the use of distributed processing system capable of handling large quantities of data. It performs batch processing on the entire dataset, generating comprehensive and accurate views or summaries of the data. The technology used for this may be Apache Hadoop.
- Speed Layer: Speed layer deals with real-time data processing. It ingests and processes the data streams in real-time, allowing for immediate analysis and low latency to incoming data. The speed layer frameworks or technologies includes Apache Kafka or Apache Spark.
- Serving Layer: Serving layer provides a unified view of the processed data from both the batch layer and the speed layer. The serving layer may use technologies like Apache HBase or Apache Cassandra.
The combination of batch processing which is slower due to the need to wait for data accumulation, but provides accurate data insights. Complements stream processing, which is faster as it allows for real-time data processing and insights, although it may not be accurate.
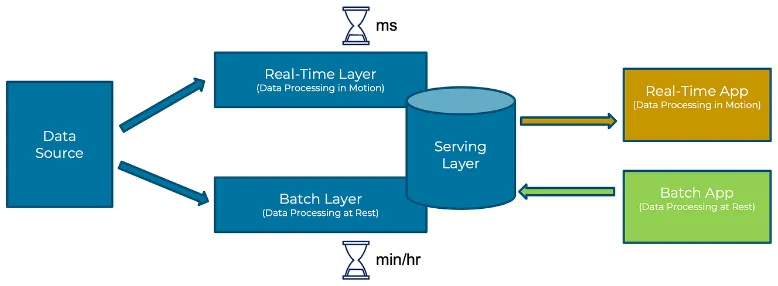
Source: https://medium.com/@bryzgaloff/how-to-implement-lambda-architecture-using-clickhouse-9109e78c718b