Cloud Services
Main Source:
- Various Google searches
- The 25 Most Important Cloud Metrics For SaaS Companies To Monitor — CLOUDZERO
- MTBF, MTTR, MTTA, and MTTF — ATLASSIAN
Terminology & Metrics
Section titled “Terminology & Metrics”The quality of cloud computing services are measured by various metrics. Some common metrics are:
-
Availability: Refer to the ability of a system to remain operational and accessible to users.
- Uptime Percentage: The percentage of time that the cloud service is available without interruptions or downtime within a specified timeframe (e.g., 99.9% uptime means the system is up 99.9% of the time).
- Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF): The average time between system failures.
- Mean Time to Repair (MTTR): The average time it takes to repair the system.
- Mean Time to Recover (MTTR): The average time it takes to restore service after a failure or outage.
- Mean Time to Resolve (MTTR): The average time to fully resolve a failure.
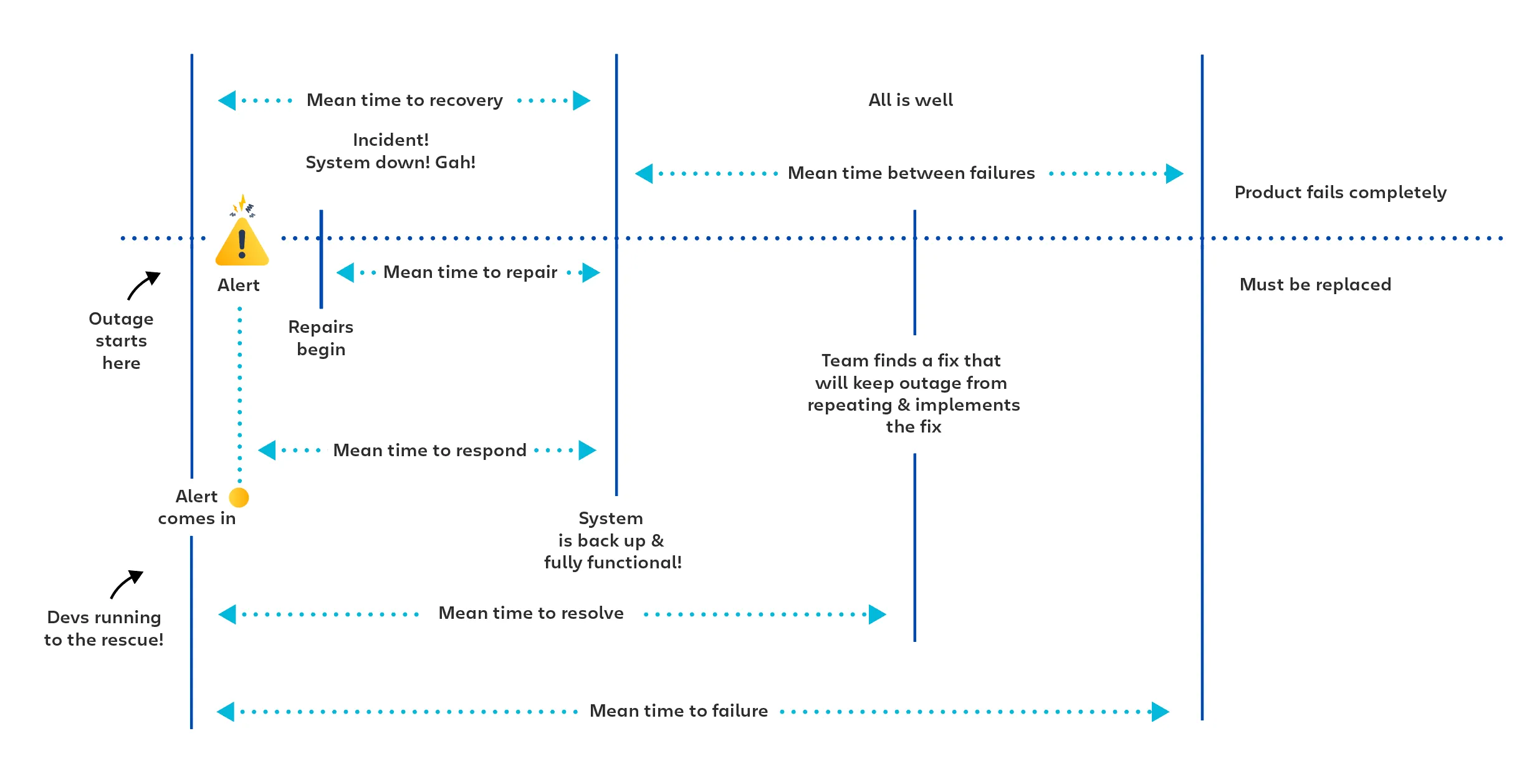
Source: https://www.atlassian.com/incident-management/kpis/common-metrics -
Performance: The speed, responsiveness, and efficiency of the system.
- Response Time: The time it takes for the system to respond to a request or action.
- Throughput: The rate at which the system can process or transfer data.
- Latency: The time delay between a request and the corresponding response.
- Bandwidth: The amount of data transferred to and from your cloud server over a given period.
- Transactions Per Second (TPS): The number of transactions or operations the system can handle in a second.
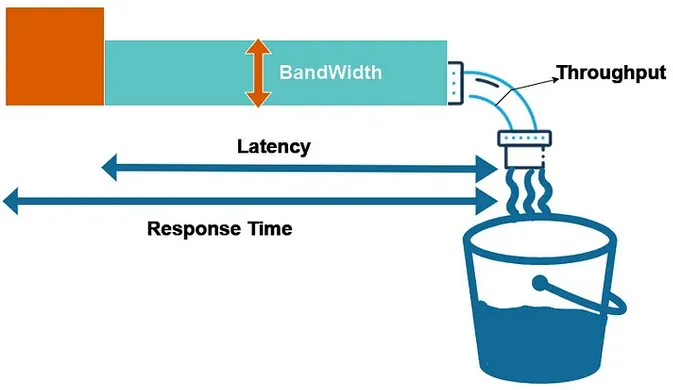
Source: https://medium.com/@sandeep15mca/latency-bandwidth-throughput-and-response-time-0ee4d9028277 -
Scalability: The ability of a system to handle increasing workloads and growing user demands.
- Vertical Scalability: The ability to increase or decrease the resources (such as CPU, memory, storage) of a single instance or virtual machine.
- Horizontal Scalability: The ability to add or remove instances or virtual machines to accommodate increased or decreased workload demands.
- Auto-Scaling Efficiency: The effectiveness and efficiency of the auto-scaling mechanisms in responding to workload changes.
-
Utilization: The extent to which computing resources are used.
- CPU Utilization: Measured as the percentage of time the CPU is actively executing instructions.
- Memory Utilization: Can be measured by the percentage of available physical or virtual memory that is actively used by running processes or applications.
- Disk Utilization: Measured by monitoring the I/O operations performed on the disk, such as the rate or the number of read or write requests.
-
Compliance: The degree of adherence of cloud providers.
- Regulatory Compliance: The cloud provider’s adherence to industry-specific regulations and standards, such as HIPAA, GDPR, or PCI DSS.
- Certifications: The attainment of certifications such as ISO 27001 (information security management), SOC 2 (security and privacy controls), or FedRAMP (for government agencies) to demonstrate compliance with specific security and privacy frameworks.
Pricing Model
Section titled “Pricing Model”Cloud providers offer some pricing model:
- Pay-as-you-go (On-Demand): Charges customer based on usage, typically on an hourly or per-minute basis. This model offers flexibility and cost-effectiveness as customers only pay for what they use.
- Reserved Instances: Customers can commit to a specific usage level for a contracted period (usually one to three years) and receive discounted pricing compared to pay-as-you-go rates. This model is suitable for predictable or steady workloads.
- Function Pricing: For FaaS services, the pricing can be based on the number of function invocations and the execution duration.
Configuration
Section titled “Configuration”Customers can configure various settings to match their needs and expectations, and these configurations will impact the price.
- Type of Services: Customer choose what services they need, such as compute, storage, networking, databases, machine learning, or serverless functions.
- Location: The location of where the services will be hosted, typically based on region.
- Tenancy: Decide how cloud services are deployed. Can be shared instances in which customer shares the same physical hardware, dedicated instances, customers are provided with their own isolated virtual machines, or dedicated hosts, customers are provided an entire physical server or host dedicated exclusively to their use.
- Compute Resources: Decide the resources, including virtual machine instance type, the number of instances, operating system, how many vCPU (virtual CPU), amount of memory, cache size, and storage capacity.
- Networking: Estimate the number of request and responses per period of time, amount of bandwidth, network performance, and scaling options for traffic spikes.
Examples of Cloud Services
Section titled “Examples of Cloud Services”The top three cloud services are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure. Below is a list of commonly used services on each of them.
Amazon Web Services
Section titled “Amazon Web Services”- Amazon EC2: Virtual servers in the cloud
- Amazon S3: Object storage service
- Amazon RDS: Managed relational database service
- Amazon VPC: Virtual private cloud for networking
- Amazon SNS: Simple Notification Service for messaging and notifications
- Amazon SQS: Simple Queue Service for message queuing
- Amazon DynamoDB: Fully managed NoSQL database
- Amazon CloudFront: Content delivery network (CDN)
- Amazon Route 53: Scalable domain name system (DNS) web service
- Amazon Lambda: Serverless compute service
- Amazon Redshift: Fully managed data warehouse
- Amazon Elastic Beanstalk: Platform as a Service (PaaS) for deploying and managing applications
- Amazon CloudWatch: Monitoring and observability service
- Amazon Glacier: Low-cost archival storage service
Google Cloud
Section titled “Google Cloud”- Google Compute Engine: Virtual machines in the cloud
- Google App Engine: Platform as a Service (PaaS) for building and deploying applications
- Google Kubernetes Engine: Managed Kubernetes service for container orchestration
- Google Cloud Storage: Object storage service
- Google Cloud SQL: Fully managed relational database service
- Google Cloud Firestore: Flexible, scalable NoSQL document database
- Google Cloud Functions: Serverless compute platform for event-driven applications
- Google Cloud DNS: Scalable domain name system (DNS) service
- Google Cloud CDN: Content delivery network for low-latency and high-throughput content delivery
- Google Cloud AutoML: Automated machine learning service for building custom ML models
- Google Cloud Vision: Image recognition and analysis service
Microsoft Azure
Section titled “Microsoft Azure”- Azure Virtual Machines: Virtual machines for Windows and Linux
- Azure App Service: Platform as a Service (PaaS) for building and deploying web and mobile applications
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): Managed Kubernetes service for container orchestration
- Azure Storage: Scalable and secure object, file, and block storage
- Azure SQL Database: Fully managed relational database service
- Azure Service Bus: Cloud messaging service for connecting distributed systems
- Azure Functions: Serverless compute service for event-driven applications
- Azure DNS: Scalable domain name system (DNS) service
- Azure CDN: Content delivery network for fast and secure content delivery
- Azure Active Directory: Identity and access management service
- Azure Monitor: Monitoring and observability service
- Azure Log Analytics: Centralized logging and analytics for collecting and analyzing data
- Azure Machine Learning: Cloud-based machine learning service for building and deploying models
- Azure Databricks: Unified analytics platform for big data and machine learning