Surfaces
Surfaces
Section titled “Surfaces”Main Source:
Surfaces is outermost layer of a 3D object that is visible to the viewer. It is the part of the object that interacts with light and is therefore responsible for determining its appearance.
Surface are represented in some ways such as:
- Implicit Surfaces
- Meshes
- NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines) Mesh
- Bezier Patches
Implicit Surfaces
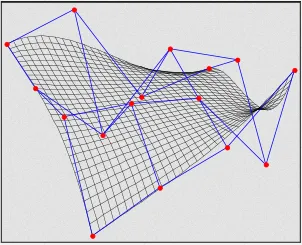
Section titled “Implicit Surfaces”Implicit surfaces, which is mathematical representation of a surface that is defined by an implicit function. Implicit surfaces can have complex and irregular shapes, and are often used to model organic or natural shapes that are difficult to represent using polygons.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Implicit_surface
Meshes
Section titled “Meshes”Meshes are used to define shape, it is a collection of vertices, edges, and faces that define the shape and topology of a 3D object or surface. These vertices together are connected and forming shape, these are called mesh types, some of them are:
- Polygon Mesh
- NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines) Mesh
Polygon Mesh
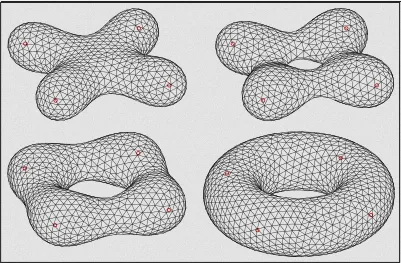
Section titled “Polygon Mesh”It is made up of a collection of polygons, typically triangles, that are connected by their edges to form a continuous surface. Those polygons are typically modeled and defined using specialized software called 3D modeling software.
Each vertices has attribute to define their position and typically specified as a set of X, Y, and Z coordinates in 3D space.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polygon_mesh
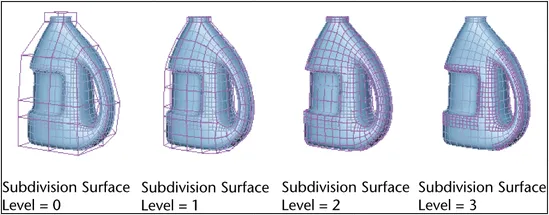
Polygonal mesh can have a smoother surface and the technique is called Subdivision. Idea behind subdivision is to take a coarse approximation of a surface, and then iteratively refine it to create a smoother and more detailed surface by subdividing the mesh into smaller sub-meshes.
One of the common used algorithm is Catmull-Clark Subdivision. It works by dividing each polygon into four smaller polygons, and then smoothing the resulting mesh to create a smoother surface.
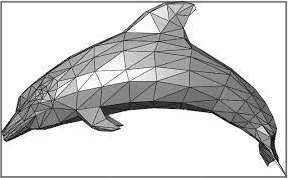
Triangular Meshes
Section titled “Triangular Meshes”Triangular Meshes are subtype of polygonal mesh which is a triangle. The reason why triangle is used because it is the simplest polygon shape which provides more flexibility. Triangle doesn’t have fixed angle making it easier to define shape such as a distorted shape or other complex shapes.
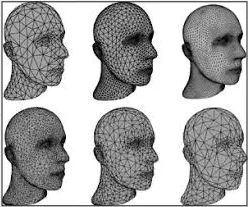
Source: https://www.graphics.rwth-aachen.de/publication/03149/
Triangle are defined using 3 vertices and edges, these vertices describe information such as position and color. Using triangle also provide us a way to represent a point called Barycentric Coordinates.
Barycentric Coordinates uses weighted sum of 3 points and we can represent a point by the combination of these 3 points. This way we can use interpolating technique to determine value or attribute of a point inside it.
For example, we determine the color by interpolating between these 3 vertices colors.
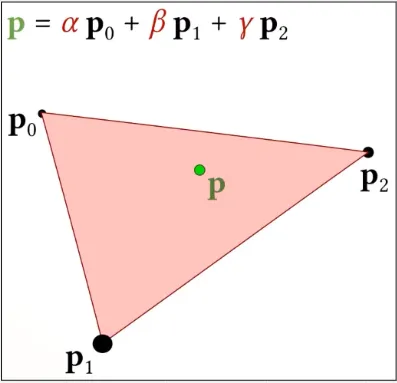
Source: https://youtu.be/HV2dKIQcp6k?t=1251
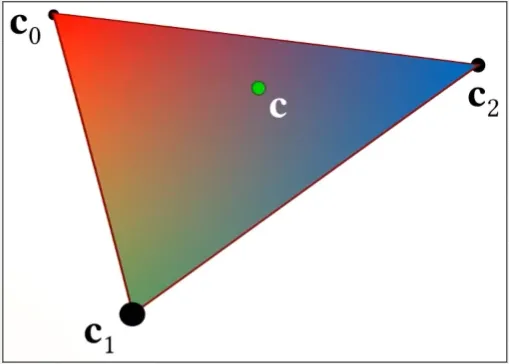
Source: https://youtu.be/HV2dKIQcp6k?t=1324
NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines) Mesh
Section titled “NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines) Mesh”A NURBS mesh is a mathematical representation of a surface that uses NURBS curve to represent the mesh. Because it’s defined using curve the main advantages is their ability to represent complex, smooth surfaces with a high degree of accuracy.
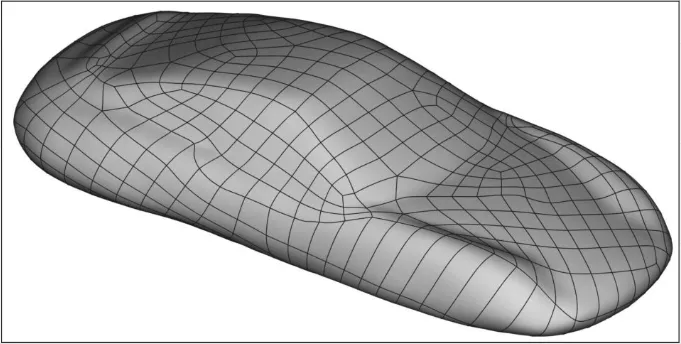
Source: https://holocreators.com/blog/what-is-the-difference-between-a-nurbs-model-and-a-polygon-mesh/
Bezier Patches
Section titled “Bezier Patches”Bezier Patches uses bezier curve to defined surface. The advantage is they can be evaluated efficiently using recursive subdivision. However, Bezier patches can be difficult to edit or manipulate directly, as modifying the control points can result in unexpected changes to the shape of the surface.