Signal Processing
Signal Processing
Section titled “Signal Processing”Main Source: Intro to Graphics 22 — Signal Processing
Signal Processing is the process of manipulating and transformation of signals, which are mathematical representations of physical phenomena such as sound, images, and data.
In signal, there are continuous time or infinite amount of information. To be able to process this, signal is sampled at a specific rate, the signal can be represented as a discrete sequence of samples, which can be more easily processed and stored.
While sampling, we only take some amount to be the representation of signal, this mean the sampled signal may be inaccurate like introducing noise into the signal.
The higher sample results in much better signal but require more bandwidth.
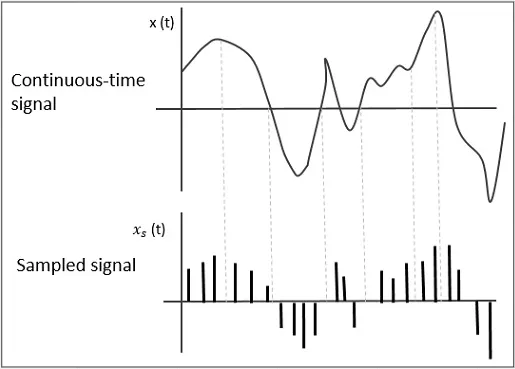
Source: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/digital_communication/digital_communication_sampling.htm
If the sampling rate is too low, it can result in aliasing, which occurs when high-frequency components of the signal are incorrectly represented as lower-frequency components. Aliasing can introduce distortion into the signal and reduce the quality of the sound.
Here, we try to approximate the missing sample but it actually causes undersampling.
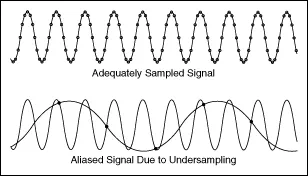
Source: https://www.ni.com/docs/en-US/bundle/labview/page/lvanlsconcepts/aliasing.html
Smooth Edges
Section titled “Smooth Edges”In raster images, the colors between pixels can be thought of as a continuous signal. The color and intensity can change rapidly or has sharp transitions between the pixel often referred as high-frequency image.
To achieve smoother appearance in raster images, we can use signal processing techniques similar to those used for smoothing or filtering signals.
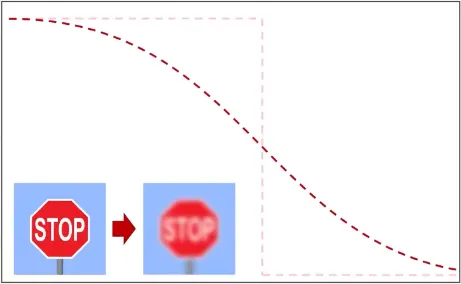
Source: https://youtu.be/UQl6ttthfXE?t=1405
This is also used in rendering when an object is aliased. The object is treated as a signal and is sampled using an anti-aliasing technique.
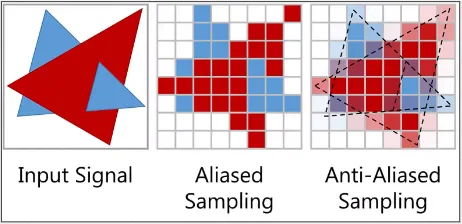
Source: https://youtu.be/UQl6ttthfXE?t=1650
Image Filters
Section titled “Image Filters”Image Filters are image processing techniques that are used to modify or enhance the appearance of an image. Image filters are typically applied to the pixels of an image in order to achieve a desired effect, such as smoothing, sharpening, or edge detection.
Image filter works by typically taking an nxn sized box of pixel called filter and the pixel inside will be transformed depending on the technique used. The transformation used to transform input into output is called convolution.
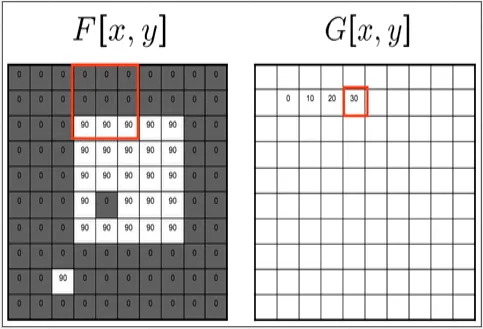
Source: https://ai.stanford.edu/~syyeung/cvweb/tutorial1.html
For example, taking a 3x3 box filter of various pixel colors, and then we take the average of those colors resulting in a blurry image.

Source: https://youtu.be/UQl6ttthfXE?t=1779
There are various image filter technique such as:
- Gaussian Filter, is used for blurring, smoothing, and noise reduction in an image.
- Sharpening Filter, enhances contrast between pixels.
- Median Filter, non-linear filter meaning the filter might change depending on the pixel in the image. Used for noise reduction in an image by taking median of neighboring pixels.
- Sobel Filter, used to detect edge.
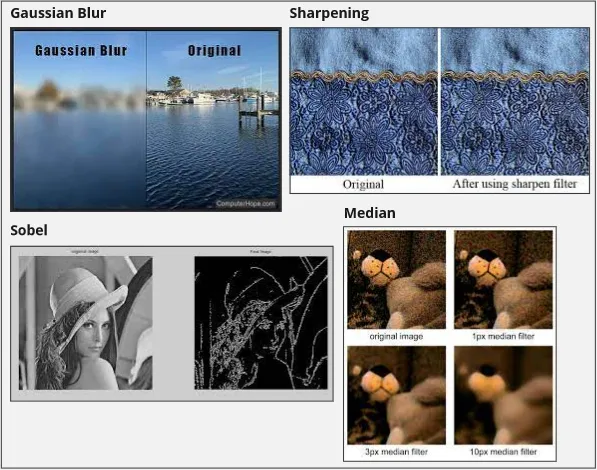
Source:
https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/p/photoshop-gaussian-blur.htm
https://medium.datadriveninvestor.com/understanding-edge-detection-sobel-operator-2aada303b900
http://community.photostockplus.com/tag/sharpen-filters/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Median_filter
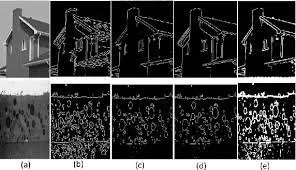
Edge Detection
Section titled “Edge Detection”Edge detection identifies the boundaries or transitions between different objects or regions in an image. The idea is edges have significant changes in intensity or color. The purpose of finding the edge is to provide important information about the structure and shape of objects in the image.
Identifying overall structure of an object is useful in many task such as robotics, video surveillance systems by detecting motion, medical imaging to detect tumor or organ segmentation.
Common methods includes:
-
Sobel Operator: It uses two 3x3 kernels to calculate the gradient of an image. The gradient is a measure of how quickly the brightness or color of an image changes in a particular direction.
-
Prewitt Operator: The Prewitt operator is similar to the Sobel operator, but it uses different kernels to calculate the gradient. The Prewitt operator is sometimes preferred over the Sobel operator because it is less sensitive to noise.
-
Canny Edge Detector: The Canny edge detector is a more sophisticated edge detection technique than the Sobel operator, and the Prewitt operator. It is able to find edges more accurately, but it is also more computationally expensive. The Canny edge detector uses a variety of steps to find edges, including:
- Gaussian Smoothing: The image is smoothed to remove noise.
- Gradient Calculation: The gradient of the image is calculated.
- Non-maximum Suppression: Edges that are not the strongest in their neighborhood are suppressed.
- Hysteresis Thresholding: Edges are classified as either strong or weak. Strong edges are kept, and weak edges are only kept if they are connected to strong edges.