DHCP
Main Source:
- DHCP Explained - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol — PowerCert
- APIPA Explained - Automatic Private IP Addressing — PowerCert
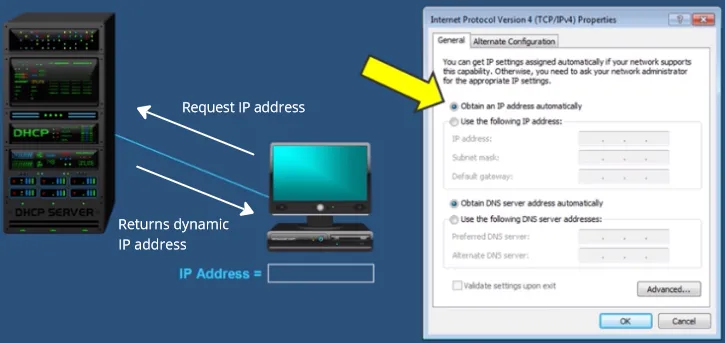
In a network, all devices are identified by IP address, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is the protocol used to automatically assign IP addresses and other network configuration parameters to devices on a network.
DHCP simplifies the process of network administration by dynamically allocating IP addresses to devices as they connect to the network, rather than requiring manual configuration of each device.
Source: https://youtu.be/e6-TaH5bkjo?si=3Kpy1MftxbzUlcfY&t=164
Static vs Dynamic IP Address
Section titled “Static vs Dynamic IP Address”An IP address that was assigned by network administrator or the user itself is called static IP address, if it’s configured automatically by DHCP, then it’s called dynamic IP address.
A static IP address provides predictability, because it can’t be changed. It may be suitable for small network. A dynamic IP address is “leased” to a device for specific period. If the address is expired, the device will need to extend the lease. This approach is flexible for larger networks where devices frequently connect and disconnect.
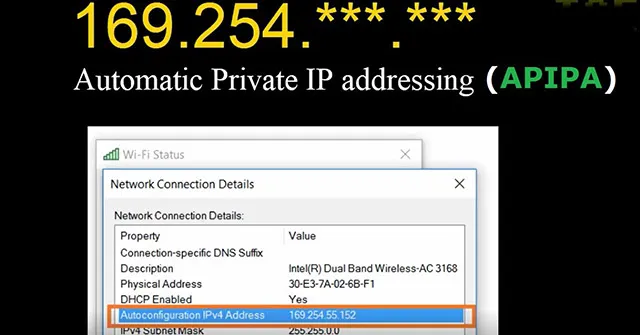
Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) is a feature in the Windows operating system that allows devices to automatically assign themselves a private IP address.
When a device are unable to obtain an IP address from a DHCP server for whatever reason, it can still obtain a private IP address. This mean the device can still communicate within the local network, but it can’t connect to the internet.
The private IP address obtained will range from 169.254.0.1 to 169.254.255.254 with a 16-bit subnet mask.